A house built around three trees. Rather than cutting down any trees on the lot, we built this house around them, enclosing them into open air courtyards. Every room in the house opens out into an outdoor space with a sheltering tree.
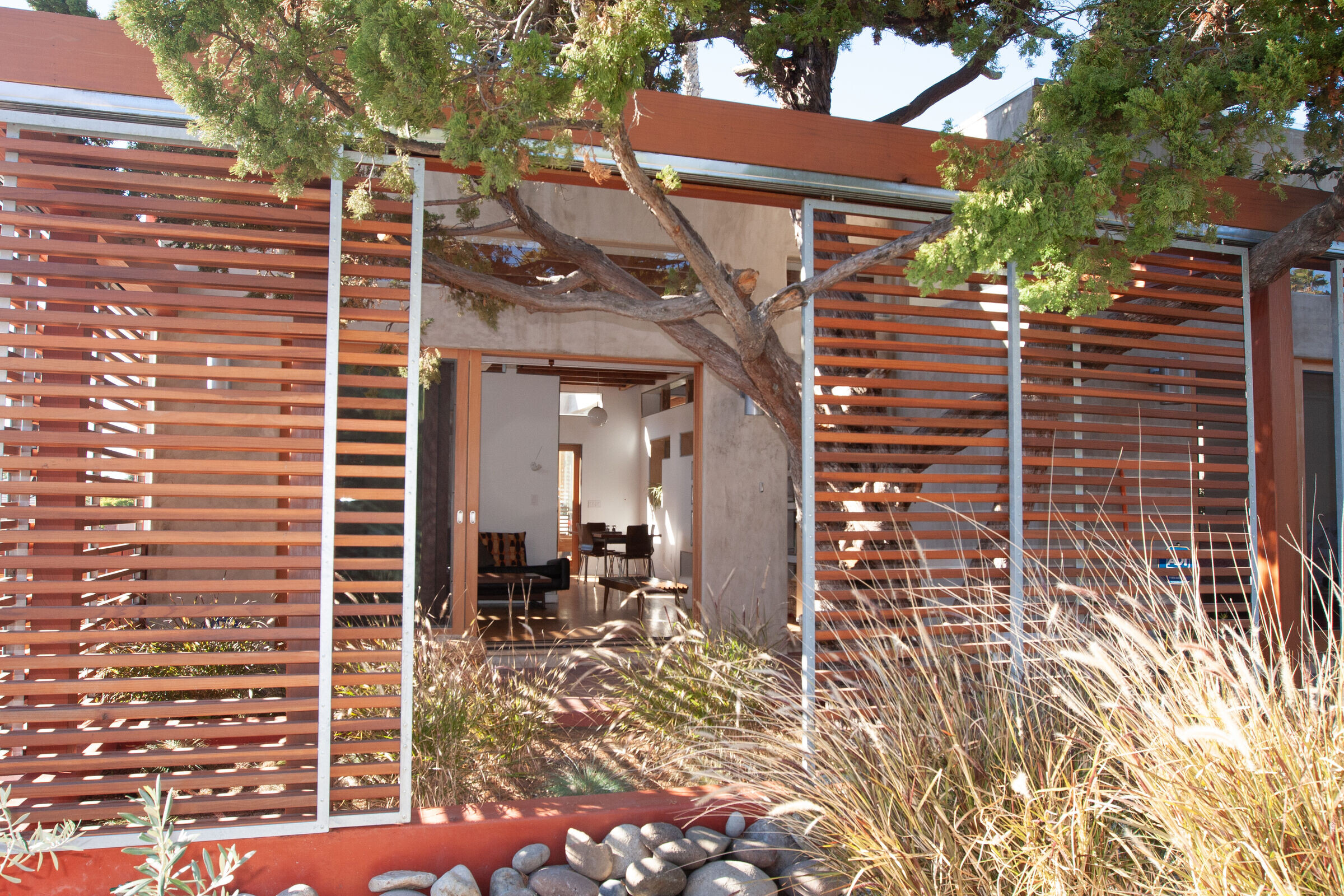

The design plays on the idea of a ‘Regional Modernism’ by merging two of the local architectural styles of the region: the thick walls and courtyards of the Spanish Colonial style and the exposed structure and open plan and glass walls of the California Case Study homes.

This is a zero-energy Passive House that produces its own solar power, heats water with solar hot water system, recycles grey water and captures rain water.

Sustainable Features:
1) Solar Power. A Photovoltaic Array provides all of the home's electrical needs. These needs are lower than most homes because of the use of passive cooling and other strategies which lower the solar heat gain and save the need to run the air conditioner

2) Solar Hot Water System
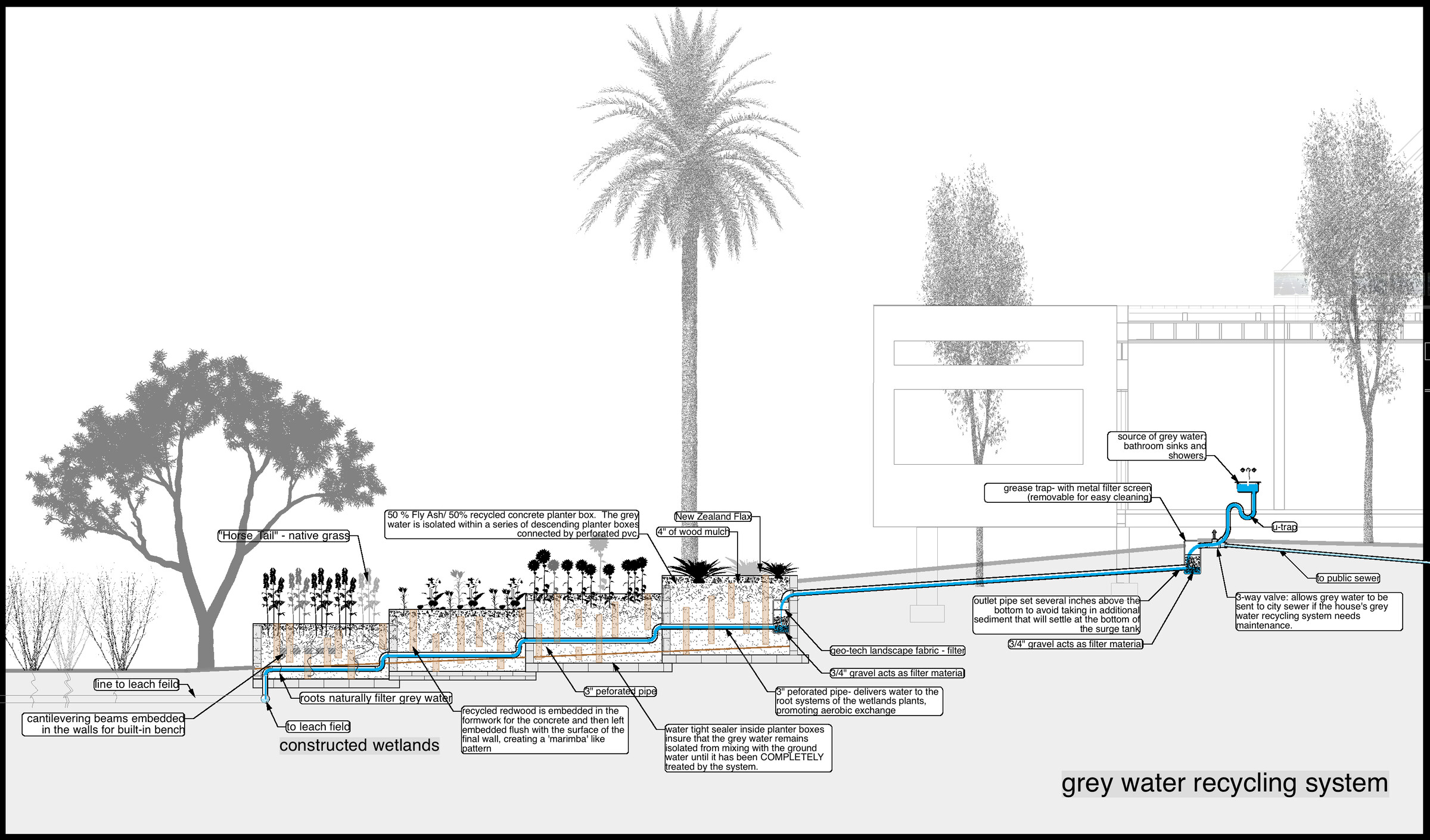
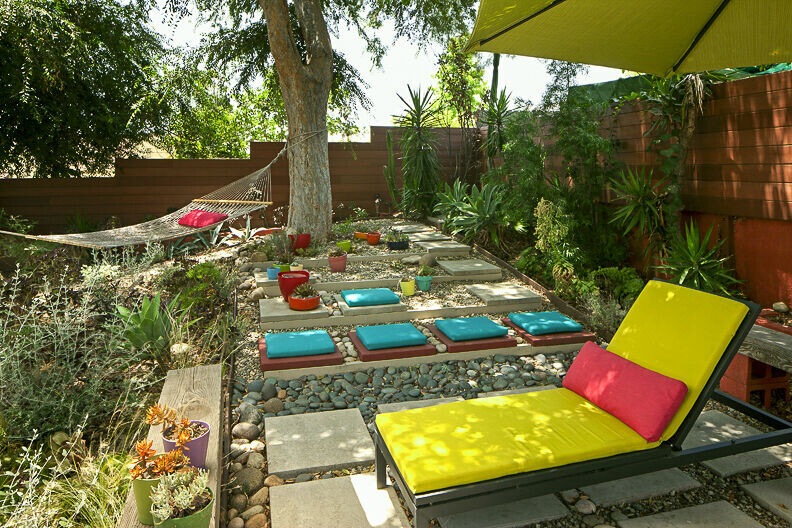
3) Grey Water Recycling System. This take water from the bathroom sinks, showers, and the washing machine, filters it, and sends it into a series of descending planters filled with plants that naturally clean the 'grey water' while creating a thriving garden.

4) Thermal Mass Wall - A stacked wall of rocks built along the South face acts a natural heat exchanger. The rocks absorb the heat during the day- before it makes it inside the house- and give it back as the air cools at night
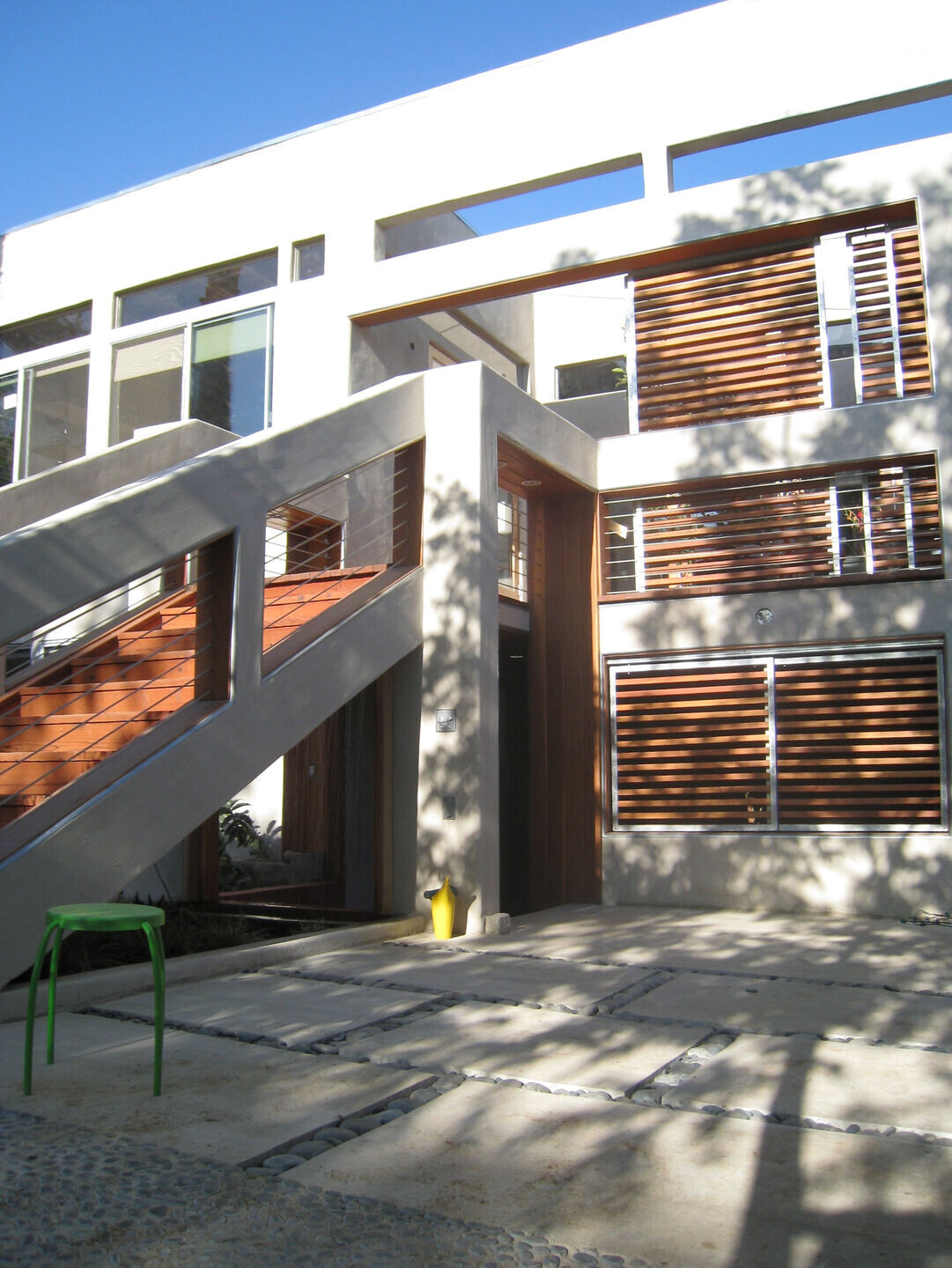
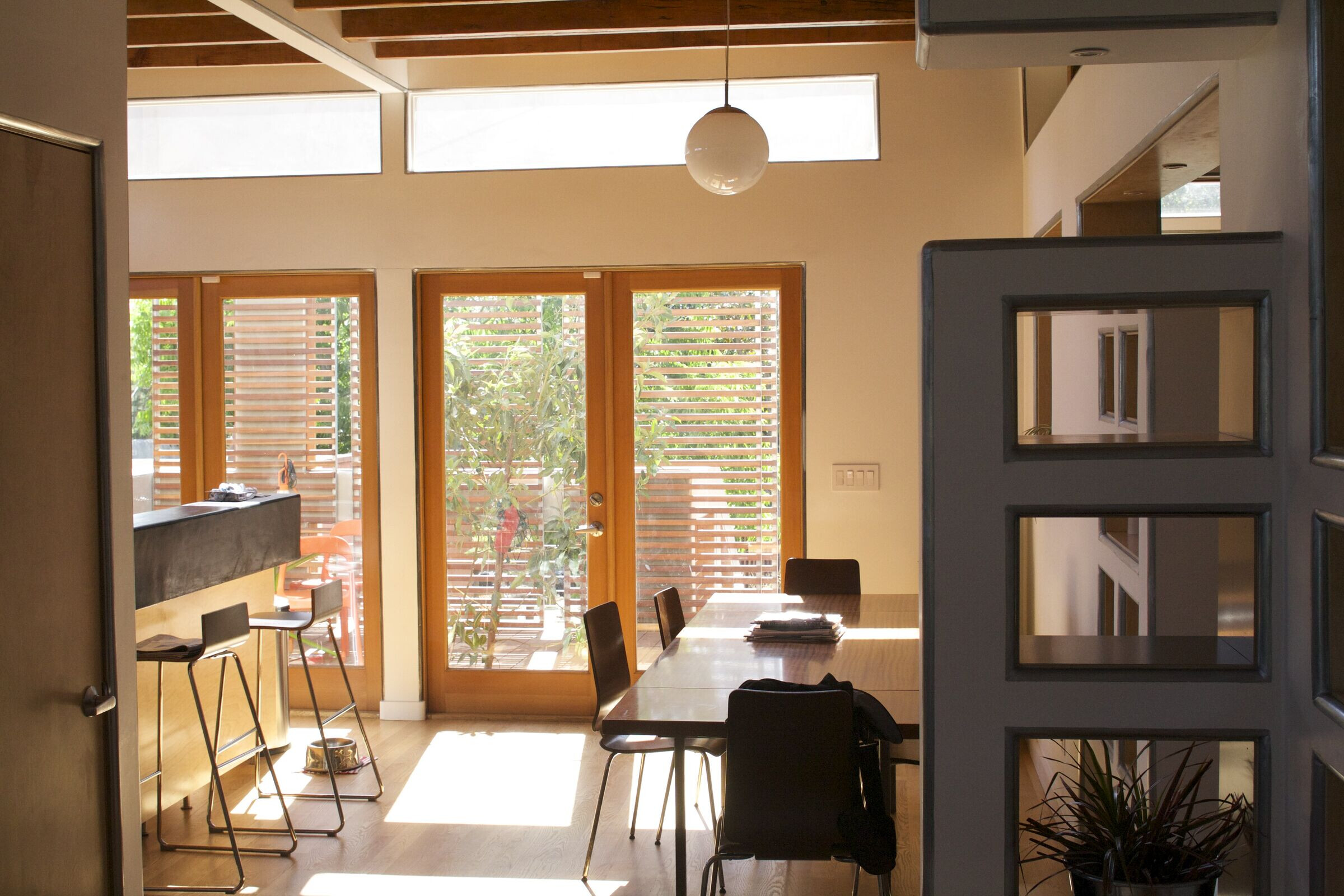
5) Mobile Shade Panel. Slatted wood panels roll across the facades on metal barn door track to control the amount of light and heat gain into the house. The mobile panels also allow the front and rear decks to be enclosed for privacy while allowing light and air to pass freely, creating a retractable facade.
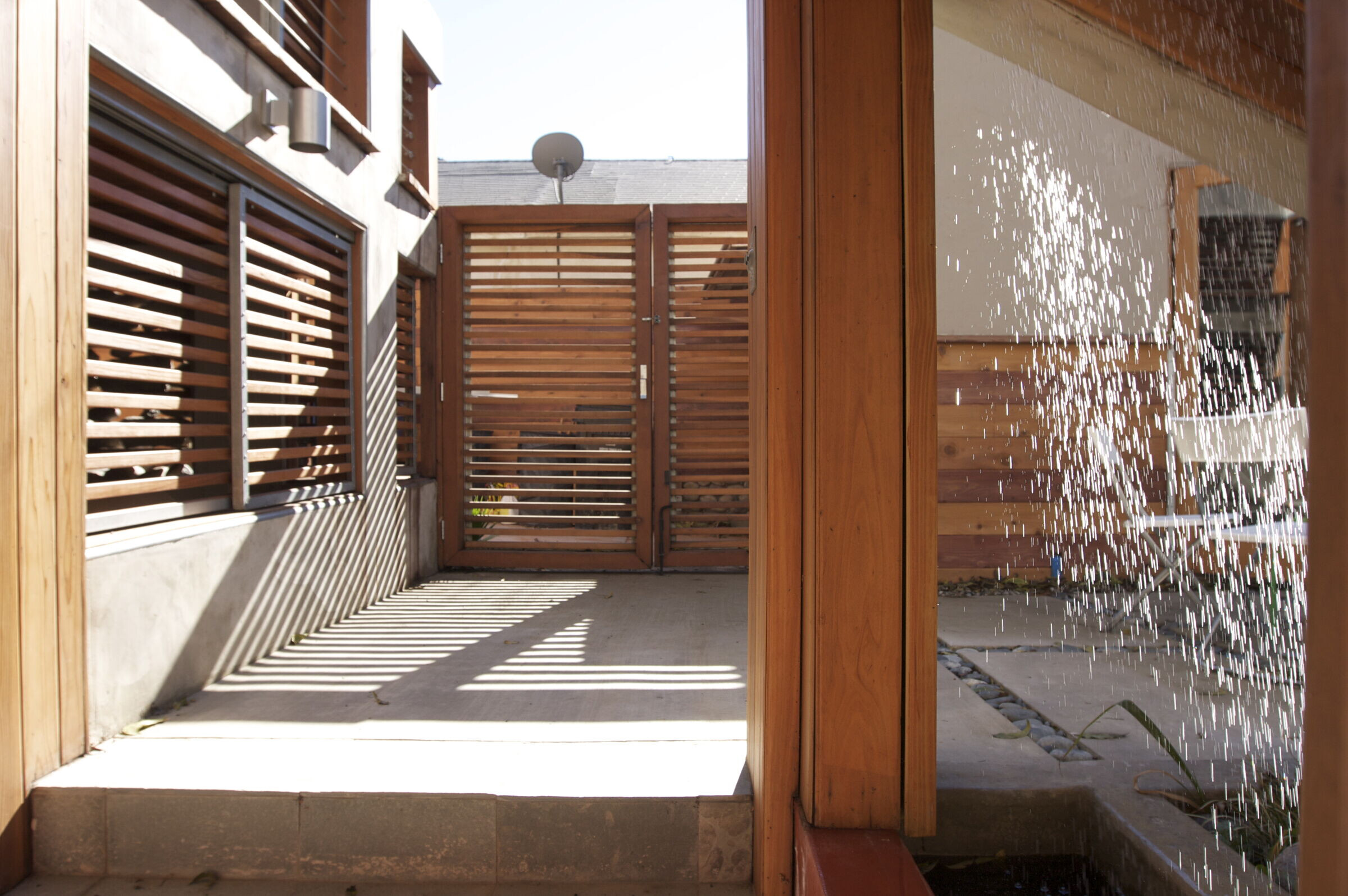

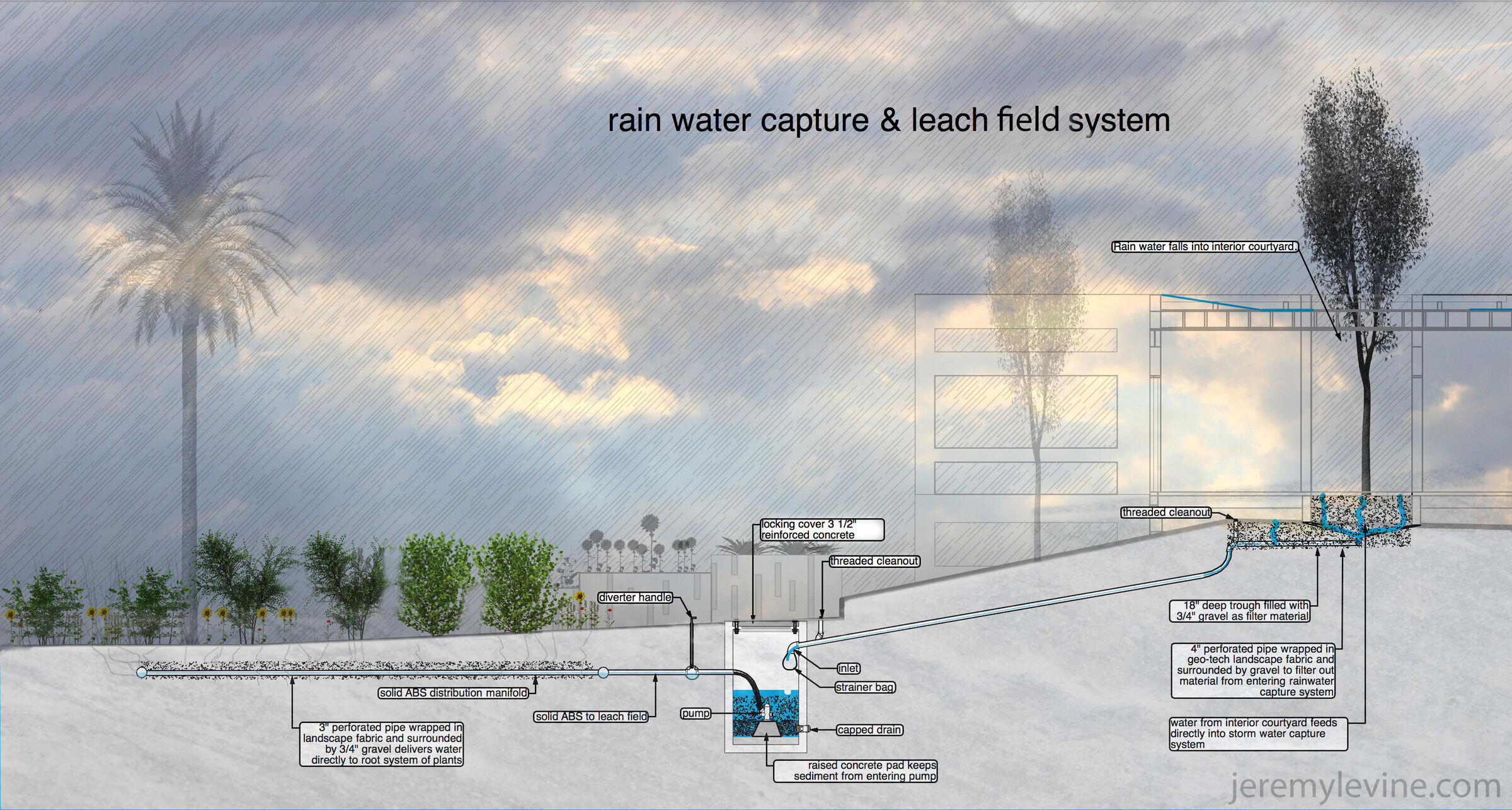
6) Rain Water Collection System - rain water is captured, cleaned through natural sand and gravel filters, and then stored in a cistern to be used to irrigate the landscaping and feed the evaporative, cooling, 'rain window'
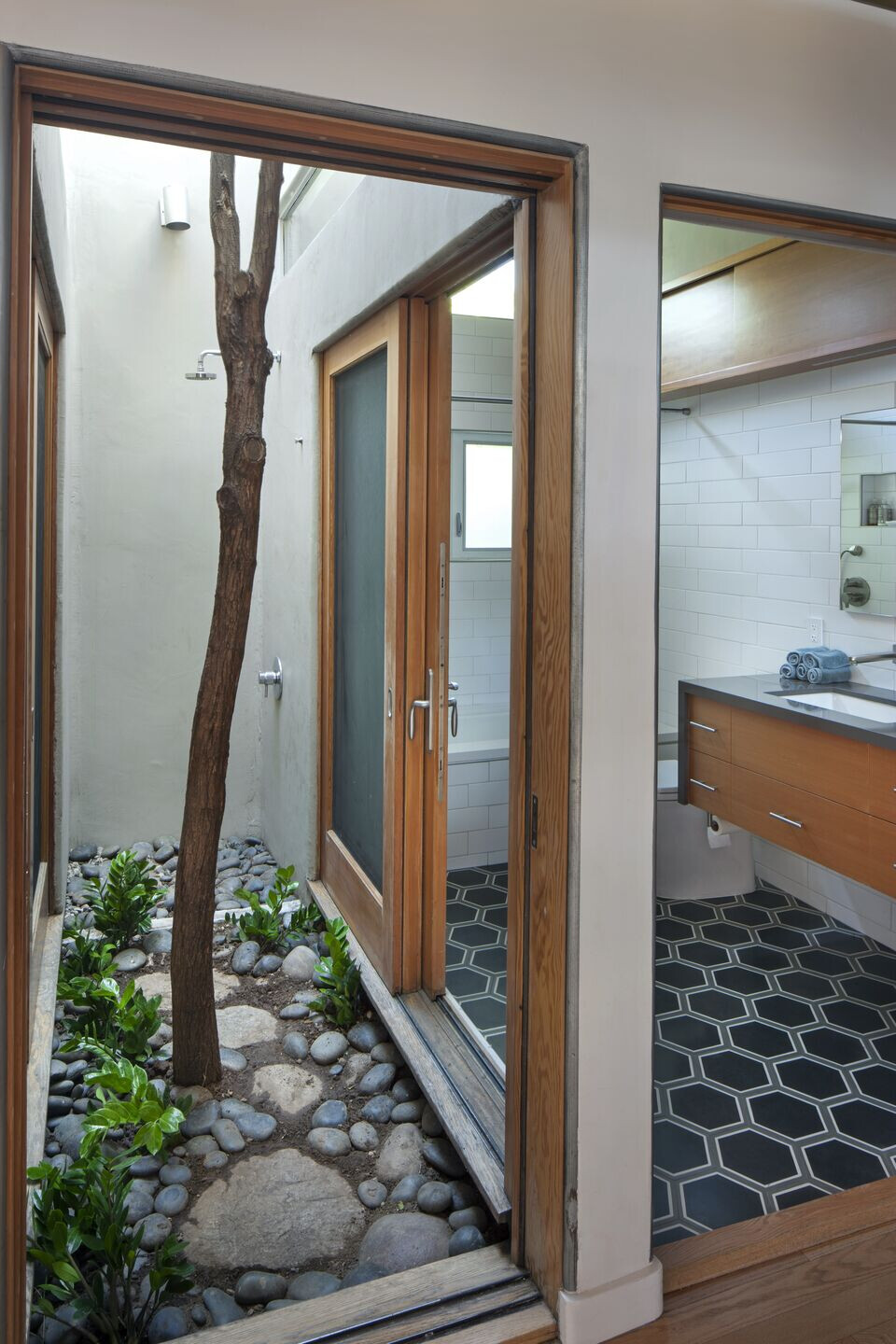
7) Thermal Chimney and the Stack Effect. The Pocket Courtyard acts as thermal chimney. A pocket courtyard with a tree inside of the house is surrounded by sliding glass doors that opento the house allowing warm air to rise up and escape abd pulling cool air in behind it. This is known as the Stack Effect.

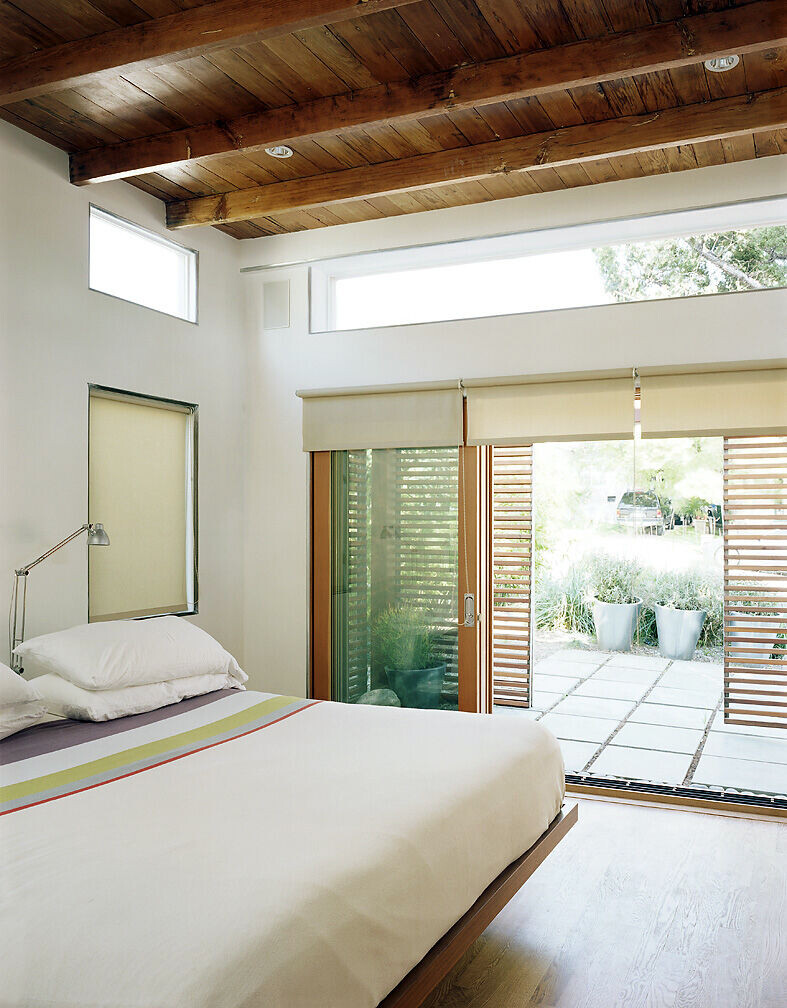
8) Passive Daylighting - By utilizing clerestory and transom windows each room in the house 'borrows' or 'shares' it's light with the adjacent spaces. This strategy of “daylighting’ dramatically lowers the need for artificial light and consequently energy consumption.
9) Recycled Fly Ash Concrete: All of the poured in place concrete baths, sink, and countertops are constructed of concrete with 50% fly ash. Note: Fly ash is the non-combustible portion of coal after it is burned in a power plant. Fly ash improves the strength of concrete and allows the use of less water, while at the same time conserving resources by recycling.
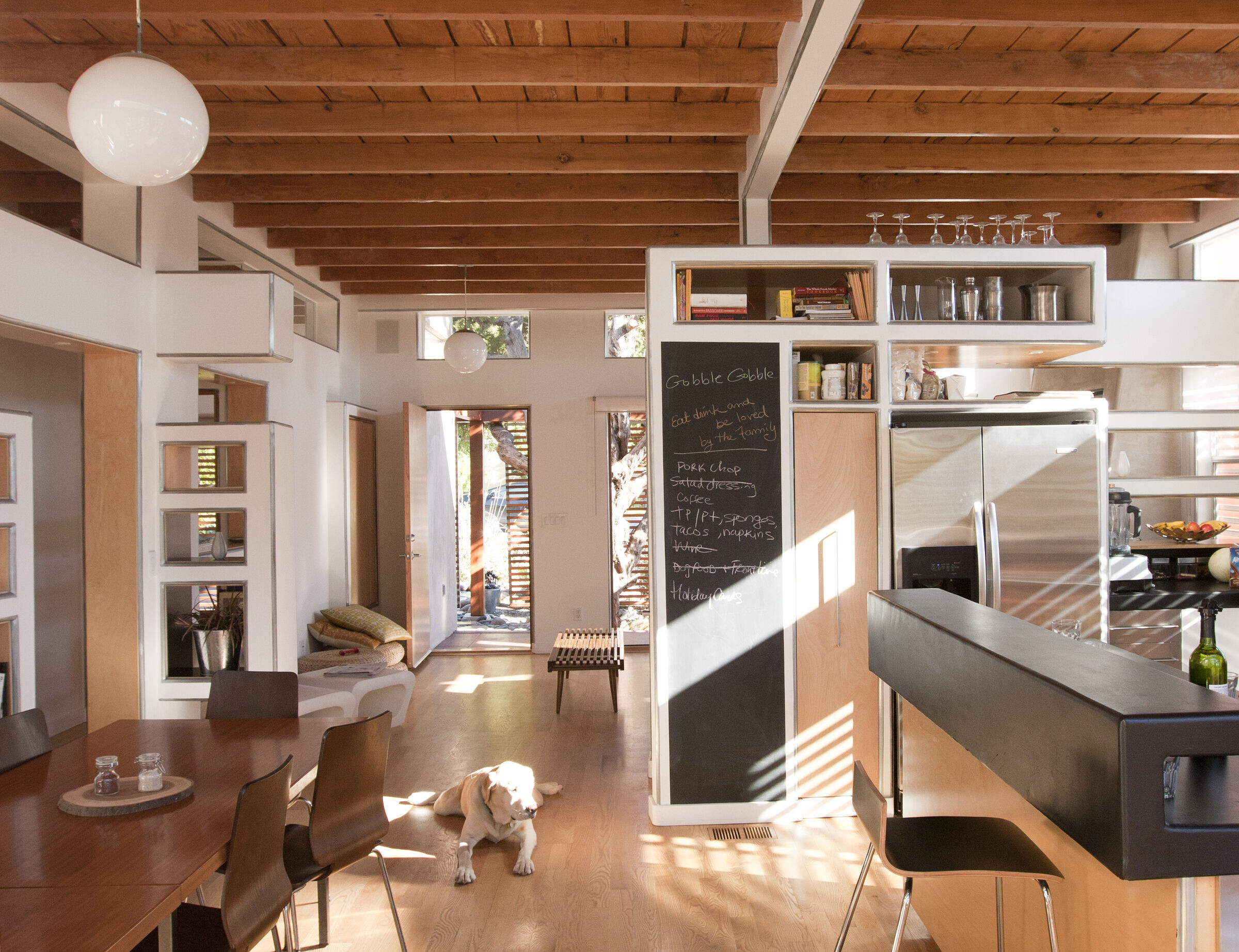

10) Reclaimed Lumber - The ceiling is made from reclaimed douglas fir salvaged during the construction. The rest of the lumber waste was recycled and turned into custom furniture for the house. (Note: One of the major sources of environmental waste comes from the demolition of buildings. Consider the gasoline consumed and the carbon monoxide exhausted by the trucks hauling construction debris.
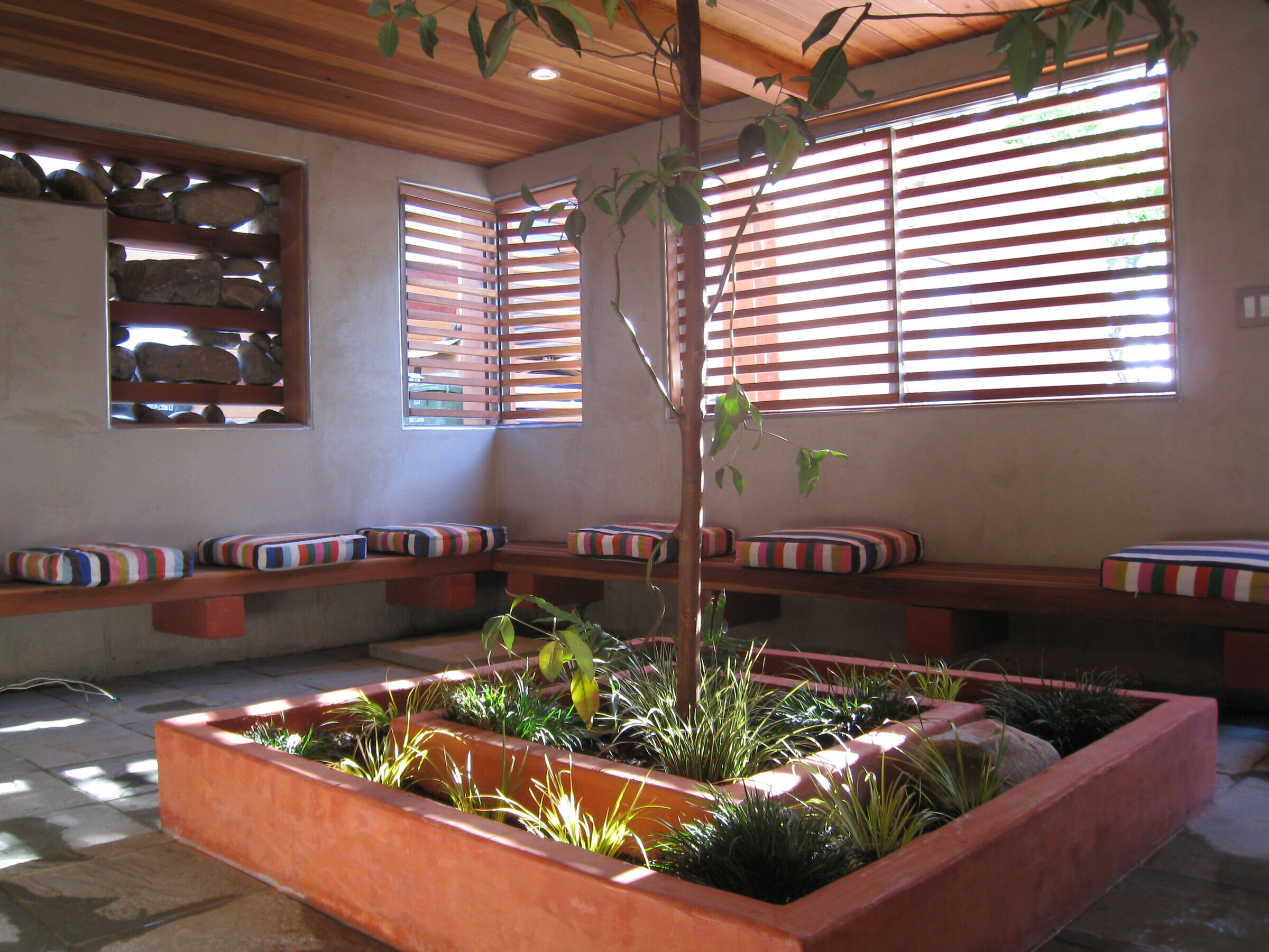

11) Efficient Space versus larger space. A smaller house uses less resources. In the bedrooms, sections of the floor can hinge upward, revealing storage undeneath. Rather than make rooms larger to accomodate bookcases, the bookcases were carved out of the walls.
12) Outdoor Shower - located inside pocket courtyard off the main bathroom. The waste water filters through a floor of gravel and into a drain that leads to the grey water recycling- system.
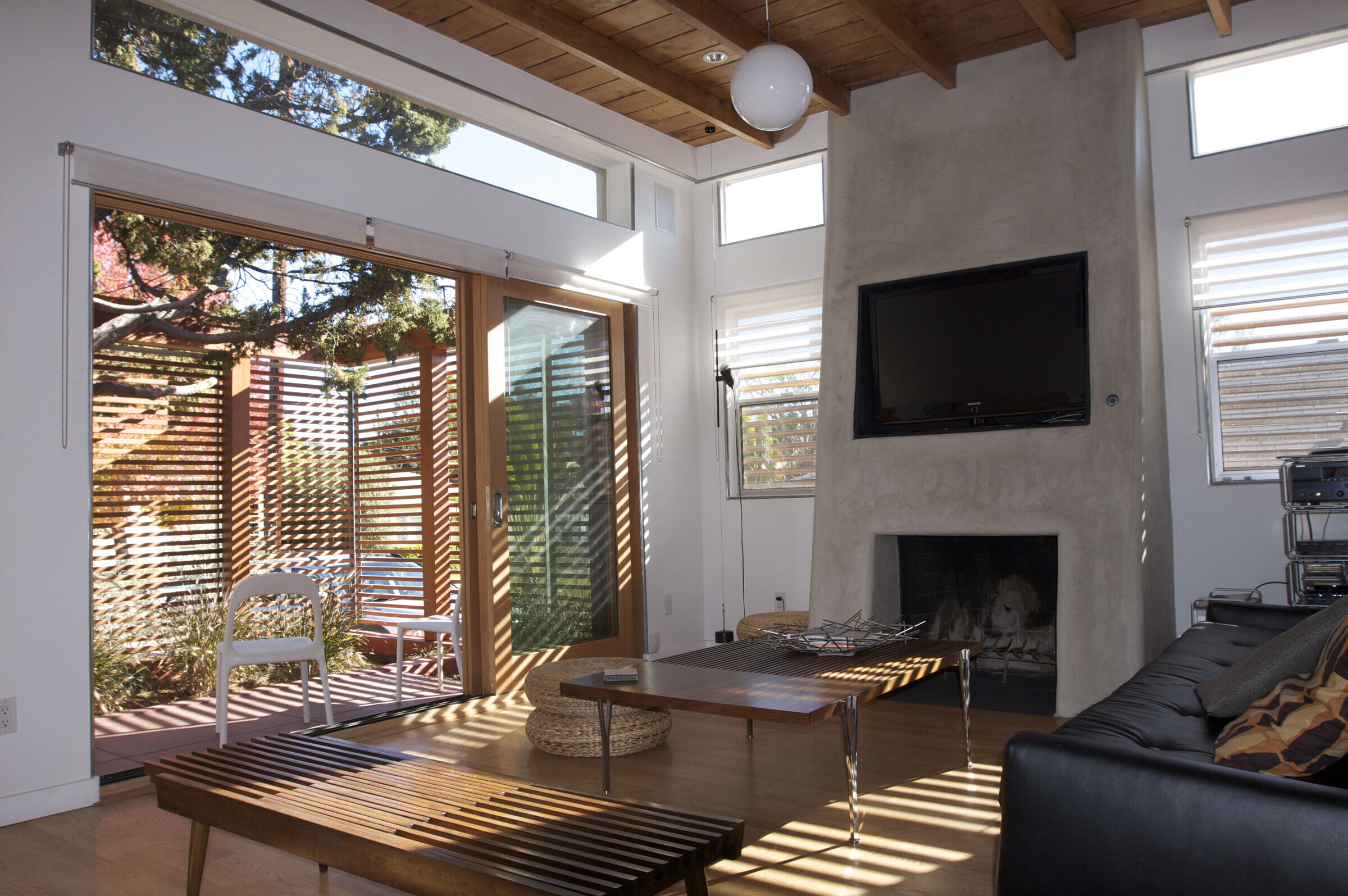

13) Passive Evaporative Cooling -Fed from the recycled rainwater system, a fountain or 'rain window’ is tucked under the staircase, cooling the downstairs through air convection created by water evaporation.
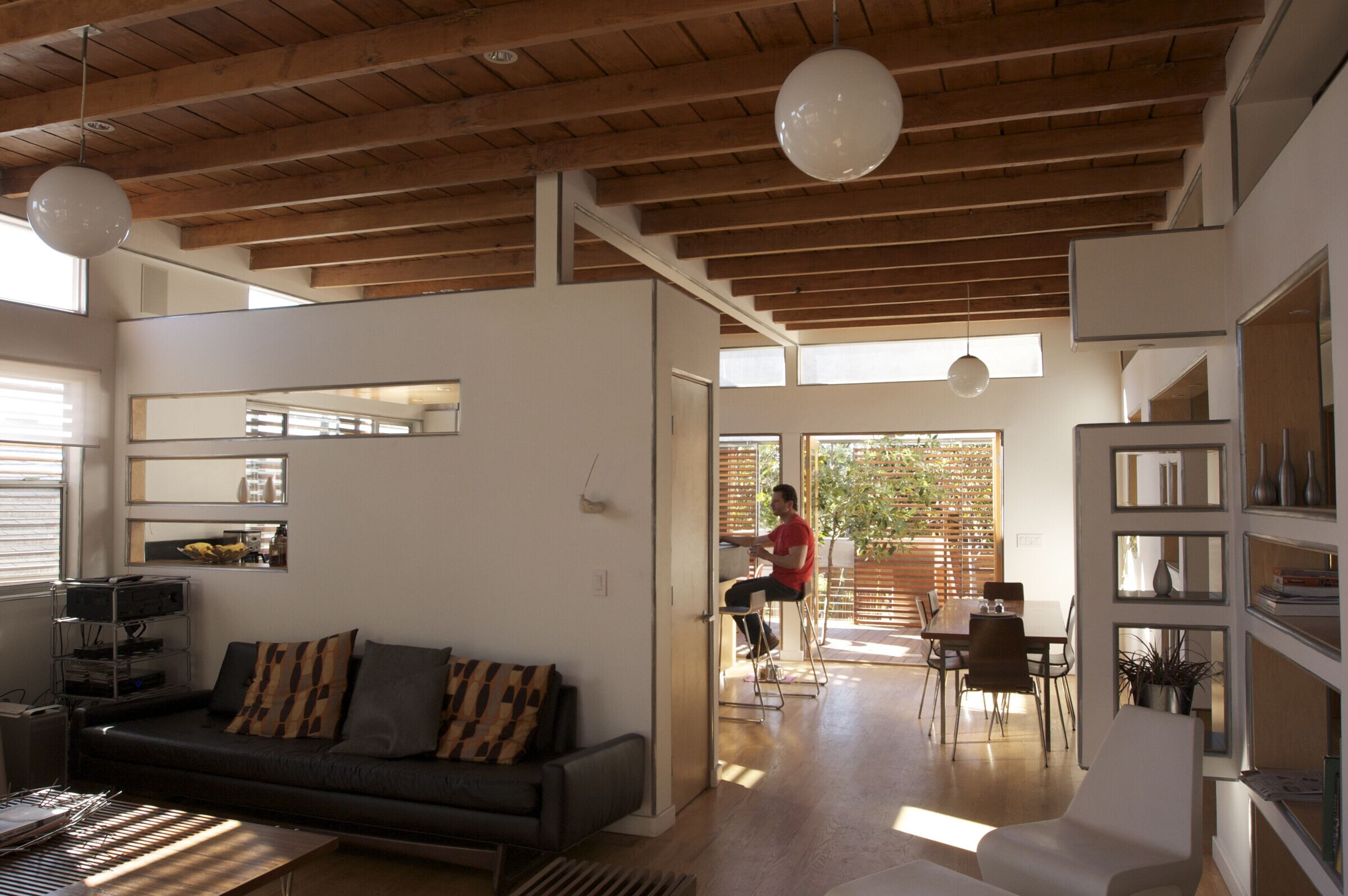

14) Xeriscaping - drought tolerant native landscaping- was used in areas that did not receive grey water or rain water. These plants are adapted to the dry desert chaparral that is native to the area.

15) Leach Field Irrigation- rather than use sprinklers we buried perforated pipes under the ground wrapped in landscape fabric and gravel in order to feed the water directly to the roots of the plants, avoiding evaporation and dramatically lowering water use

16) Passive Climate Control - Create breezeways through house with large ceiling fans instead of using AC.
17) Poured in place concrete countertops in the kitchen and bathrooms, instead of less sustainable options like stone or tile.

18) Non VOC Paints and Stains
19) All plumbing fixtures are low-flow energy efficient

20) All electrical appliances are energy star rated
21) All lighting is LED or CFL compact fluorescent