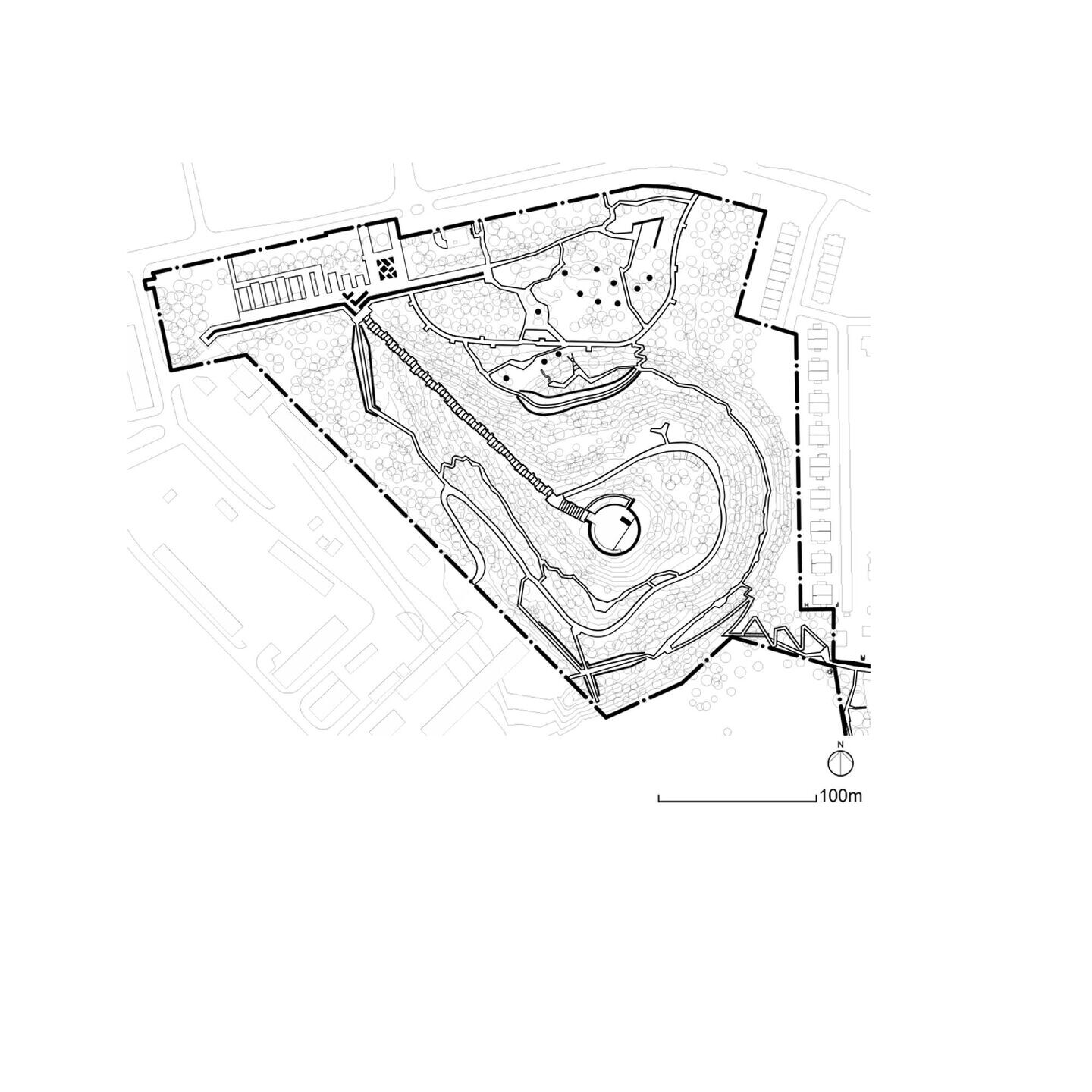
The Warsaw Uprising Mound Park is the Fourth Nature refuge created on an anthropogenic hill. For years, this site served as a repository for the debris from Warsaw after the city was destroyed in World War II, gradually giving rise to an artificial hill that now stands 35 metres above the surrounding flat and marshy landscape. After the landfill was closed in the mid-1960s, the hill became overgrown with vegetation that, over time, transformed into a ruderal "forest". Its adaptation into a public park involved recognising its ecological and symbolic potential and making various uses of the rubble found on site. The Mound area was thus reclaimed in three different ways: symbolically, physically and by the Fourth Nature:



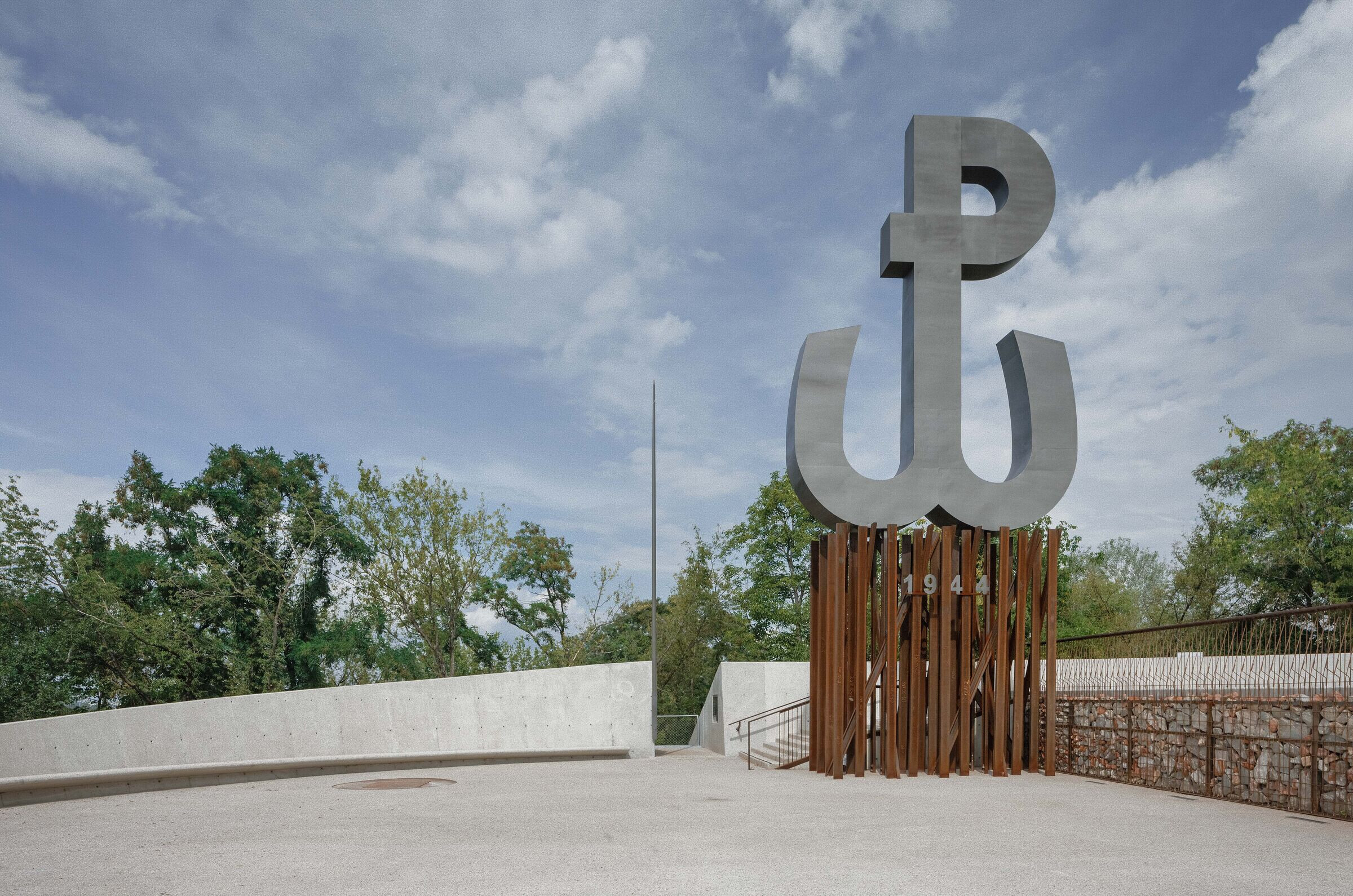
Reclaiming the meaning.
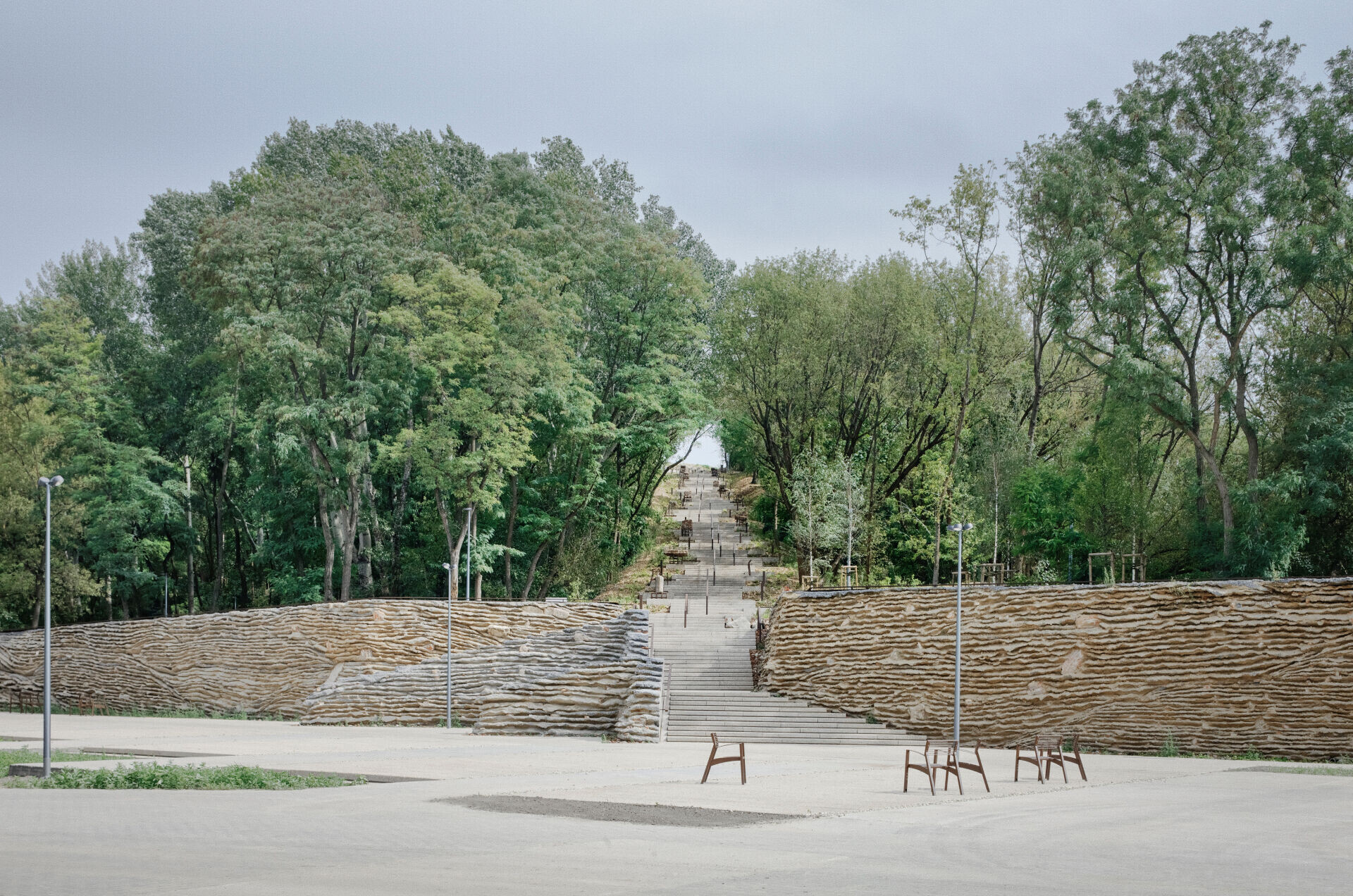
In 1994, a former participant in the Warsaw Uprising and an architect, Lt. Col. Eugeniusz Ajewski "Kotwa", recognised the symbolic potential of the landfill. He and other veterans initiated the erection of a monument on the top of the hill. According to Ajewski, the remaining area was to be used for recreation. In 2019, our team won a competition for the project, which would befit the site's significance and provide a recreational space for the residents of the newly constructed housing estates in its vicinity.
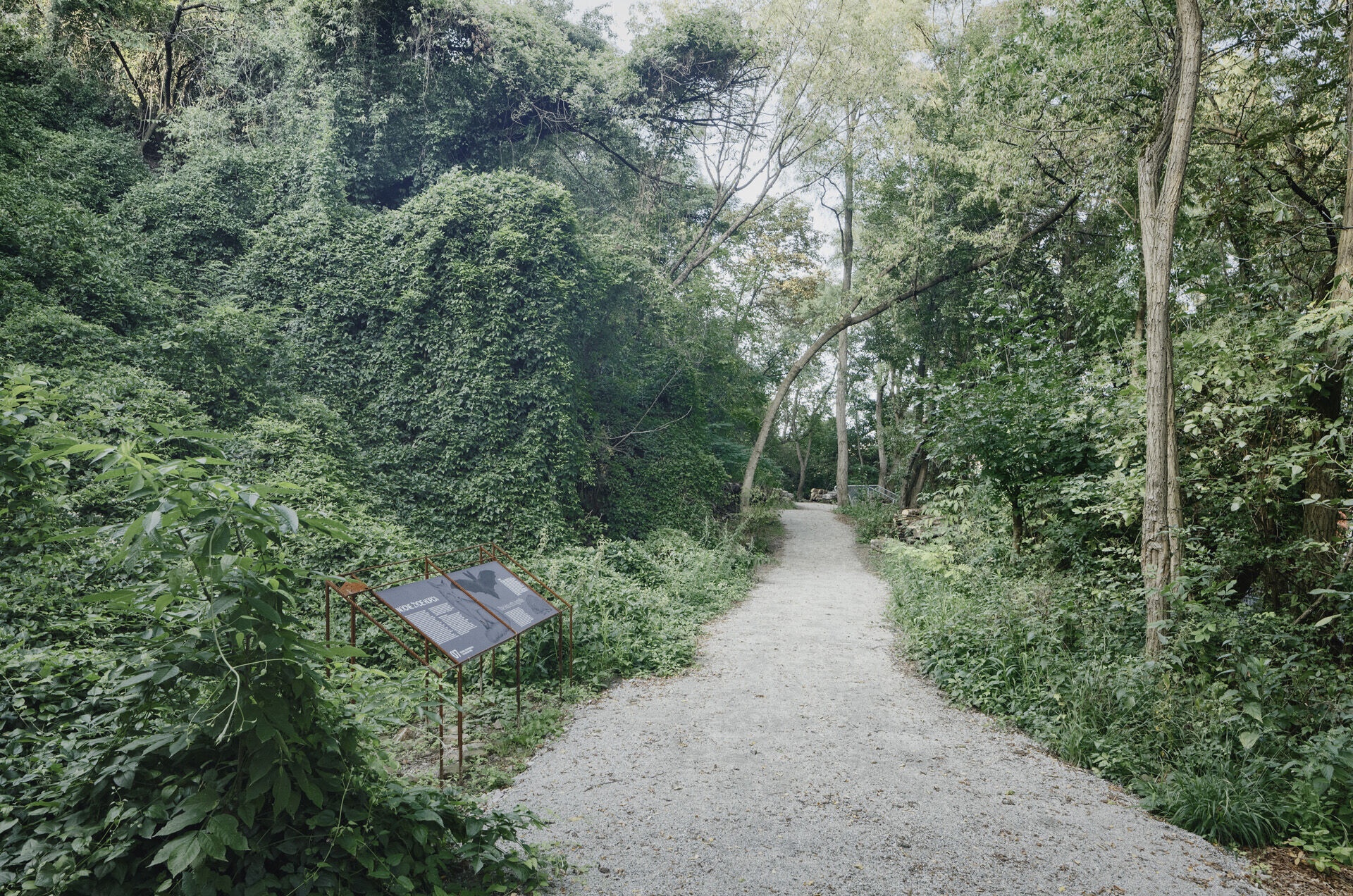
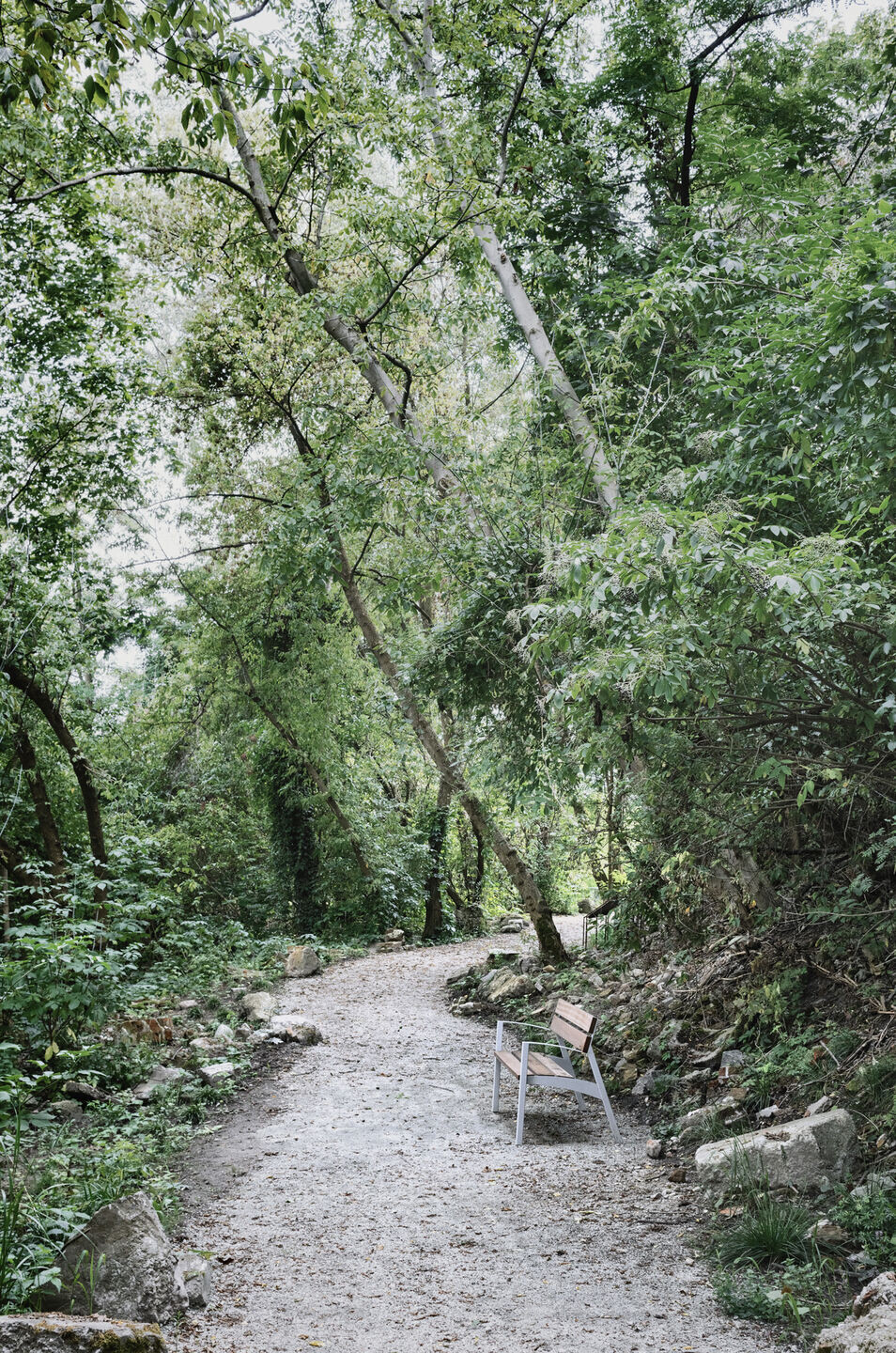


Reclaiming by the Fourth Nature.
The Mound is a degraded area, a brownfield, a wasteland reclaimed by the Fourth Nature. The project's starting point was observing natural processes initiated by pioneer and invasive species and further modelling them to increase biodiversity. This can lead to a change in the paradigm of aestheticising urban nature in favour of exposing its authenticity. The adopted environmental strategy includes, among others:
1. Supporting the natural succession process.
2. Increasing biodiversity through new plantings.
3. Supporting the soil-forming process by retaining organic matter and surface water runoff.
4. Introducing micro-retention (wooden gutters, fascine drains).
5. Creating ecological niches for small animals.
6. Introducing bioreceptive rubble concrete.
A meadow that grew over the ruins of Warsaw in 1945 was sown again on the rubble fields, and its species composition is known thanks to the pioneering historical publications of Prof. Roman Kobendza.
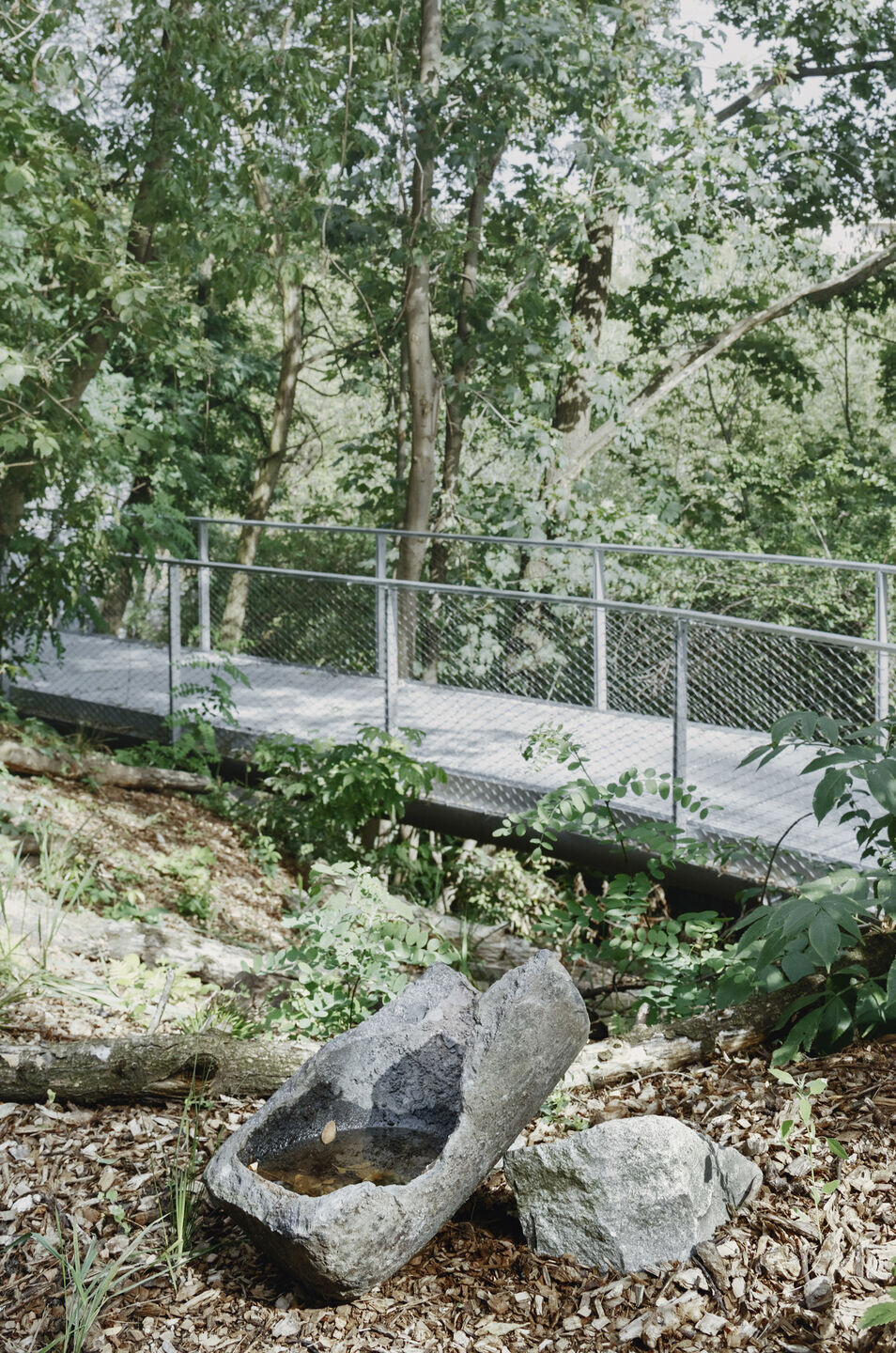


Reclaiming rubble.
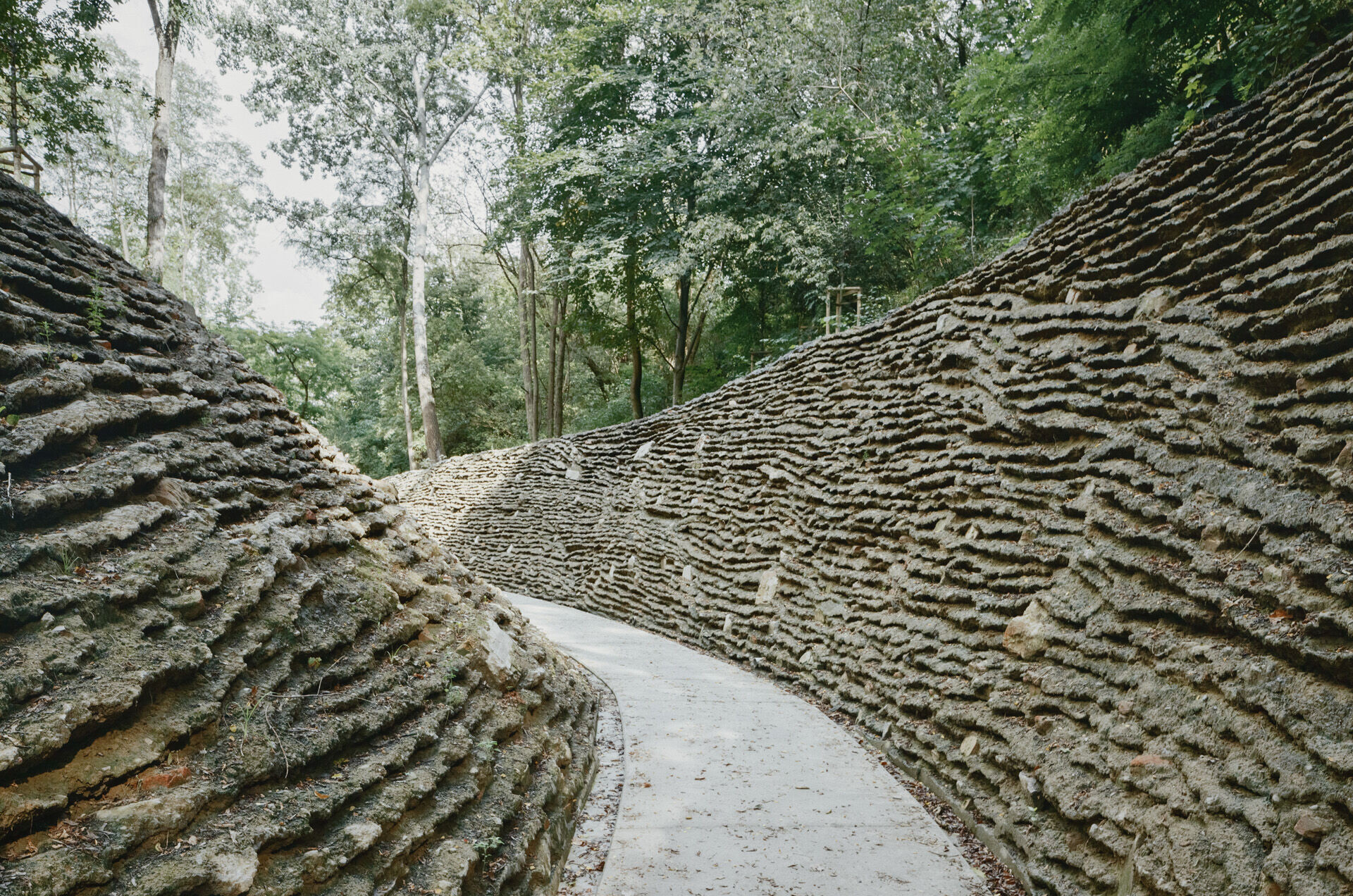
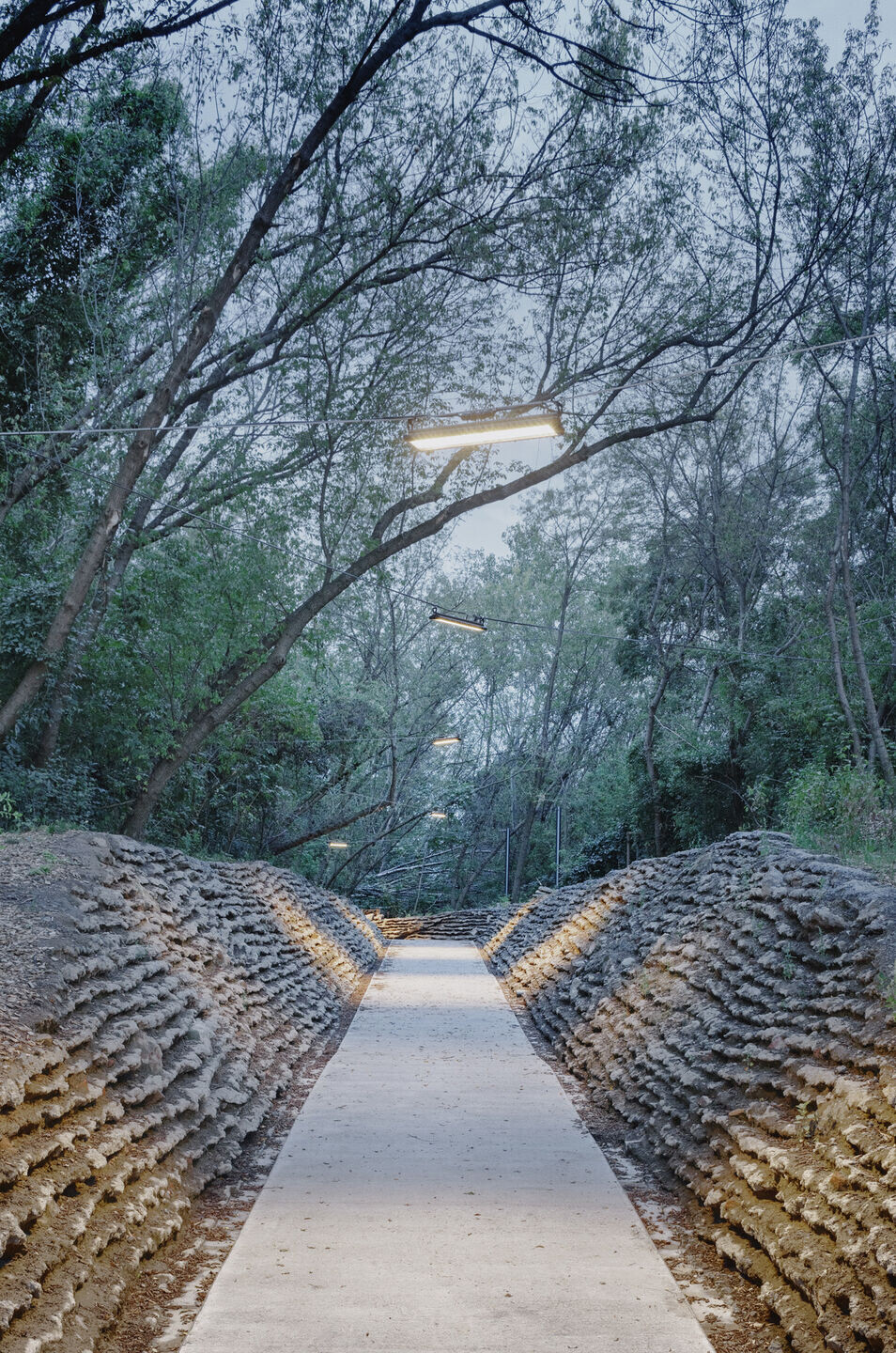
The enormous amount of debris in post-war Warsaw was a problem but also a resource—the raw material for producing rubble concrete blocks from which numerous buildings have been built. Warsaw became a precursor of the circular economy; we wanted to refer to this heritage. Our project implemented several strategies for recycling rubble extracted during earthworks, all of which, following the conservator's decision, remained on site:
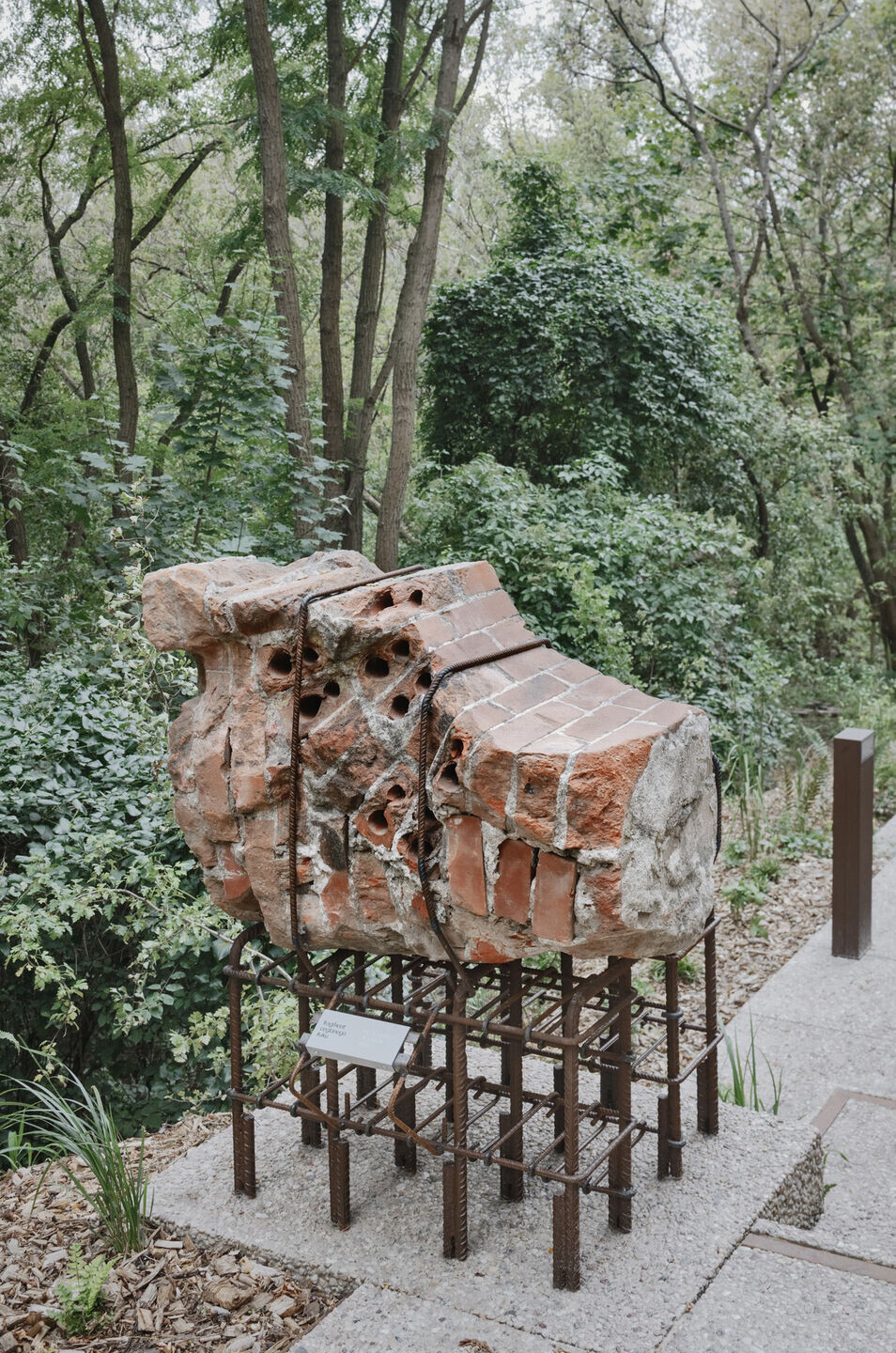


1. The most important was an innovative technology for producing modern rubble concrete, which forms the ravines' retaining walls and the Mound's base. Over time, this local anthropogenic rock, Warsaw urbanite, will be covered with moss and gradually assimilated by surrounding nature. Before that happens, we can see the remains of old Warsaw embedded in rubble concrete: bricks, stove tiles and balusters.
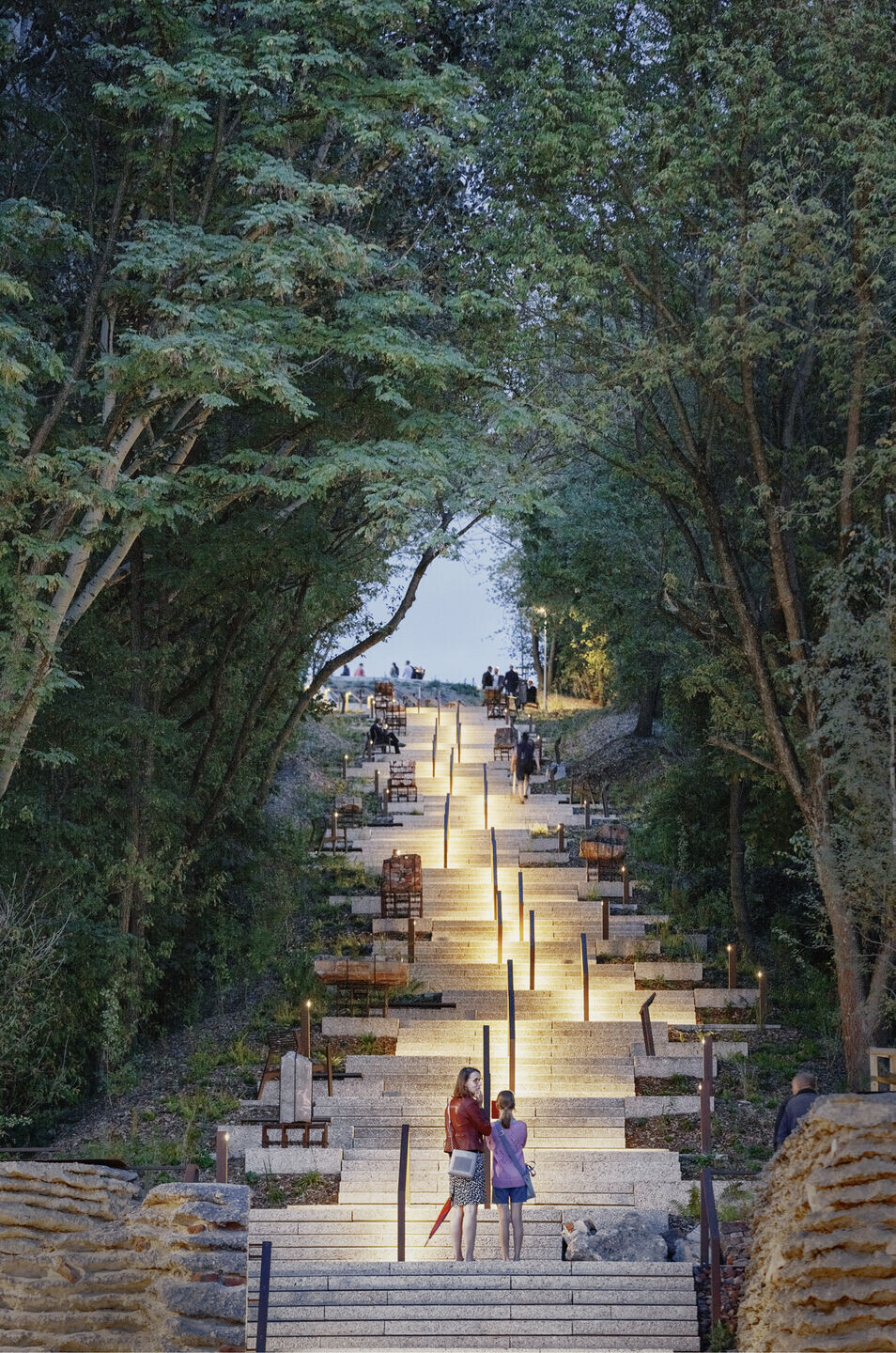


2. Another strategy was to repurpose the rubble as filling material for the gabions in the Lapidary, designed as a labyrinth of "ruins".
3. The fair-sized remains of destroyed buildings were labelled and displayed within the park and along the grand avenue leading to the main monument on top of the hill.